A New Design Of Conformal Cooling Channels (Milled Groove Square Shape) In Injection Molding Processes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
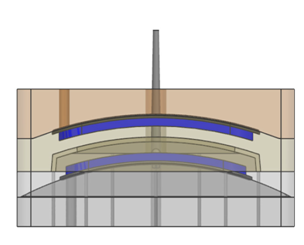
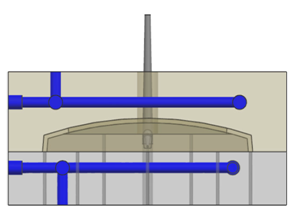
In materials processing, quality and productivity are notably important and must be controlled for each product type produced. In the injection molding process, quality is measured as the extent of warpage of molded parts and productivity is measured in terms of the molding cycle time. This paper presents a new design of milled grooved square shape (MGSS) conformal cooling channels, which provide more uniformity in cooling with a larger effective cooling surface area compared to circular and other types of cooling channels with a similar cross-section. This study examined the warpage of molded parts and the cooling time, which affected the molding cycle time.
A case study involving a front panel housing was performed, and the performance design of the MGSS conformal cooling channels were compared to that of conventional straight-drilled cooling channels by simulation using Autodesk Moldflow Insight (AMI) 2013 and validated experimentally. The simulation and experimental results are in good agreement for the MGSS conformal cooling channel, which was able to reduce the warpage and cooling time of the molded part by 13.95 to 54% and 64.83%, respectively, compared to straight-drilled cooling channels.
|
|
Keywords:Injection Moulding Process; Polymers; Conformal Cooling Channels |
|
|
|