- Category: PENYELIDIKAN SLIDER
Mycoremediation of Malaysian Rubber Wastewater By Non-Pathogenic Fungi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
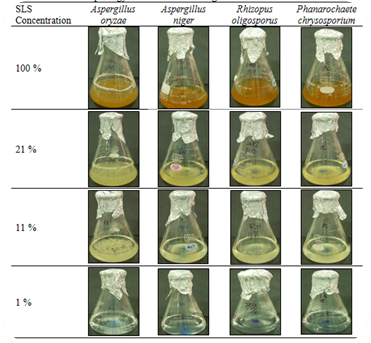
Skim latex serum is the liquid waste from industrial latex concentrate processing industry that is rich in BOD, COD, and rubber particles. The discharge of this effluent into the environment without proper treatment can affects the ecological system which human health ultimately depends on. Therefore, a study was conducted with an objective of treating this industrial effluent through biological approach or mycoremediation. This mycoremediation treatment method focuses on evaluating the capability of non-pathogenic fungi namely Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus niger, Rhizopus oligosporus, and Phanarochaete chrysosporium to grow independently in the liquid waste thus directly carrying out the remediation process. Among the four fungi, Aspergillus oryzae gave the highest biomass growth in the wastewater thus yielded significant reduction in total solids (15.6%), suspended solids (10.3%), dissolved solids (47.6%), BOD (67.8.6%), and COD (62.6%) after just three days incubation. Therefore, it could be suggested that the Aspergillus oryzae could be one of the potential fungal strain to be used in bioremediation of industrial rubber effluents.
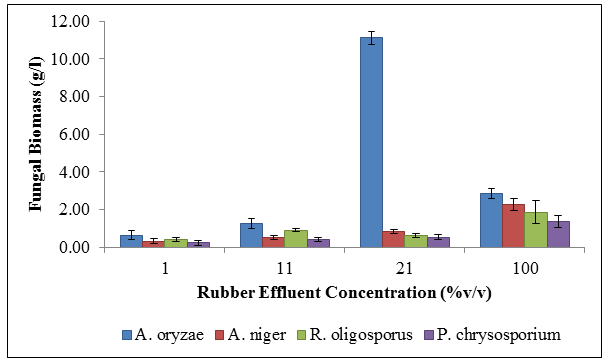
Figure 1: Fungal biomass yield in undiluted and diluted rubber effluent. Data are expressed as Mean±Standard Deviation (n=3). After 5 days of incubation time, among all of the fungi, Aspergillus oryzae gave the highest yield in all SLS concentrations with 21% of SLS gave the maximum biomass yield of 7.8 g/g
|
|
|
Keywords: Aspergillus Oryzae, Bioremediation, Latex Concentrate Effluent, Skim Latex Serum, Natural Rubber. |
|